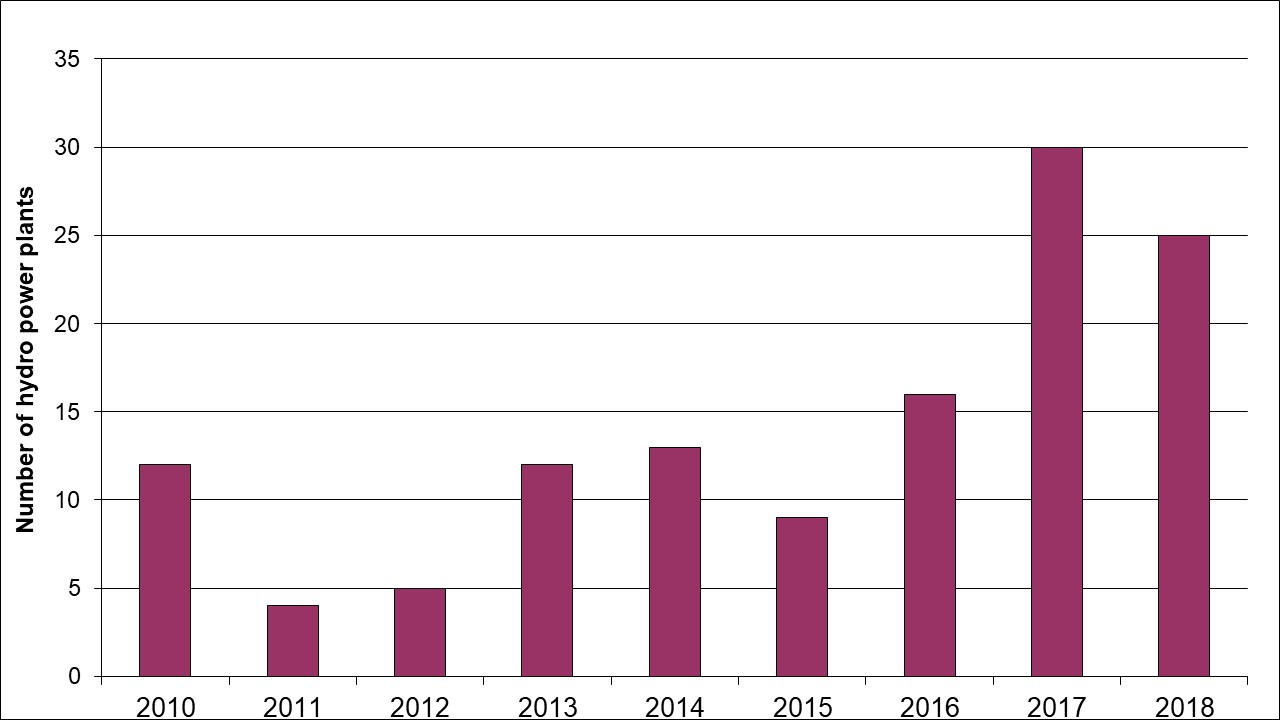
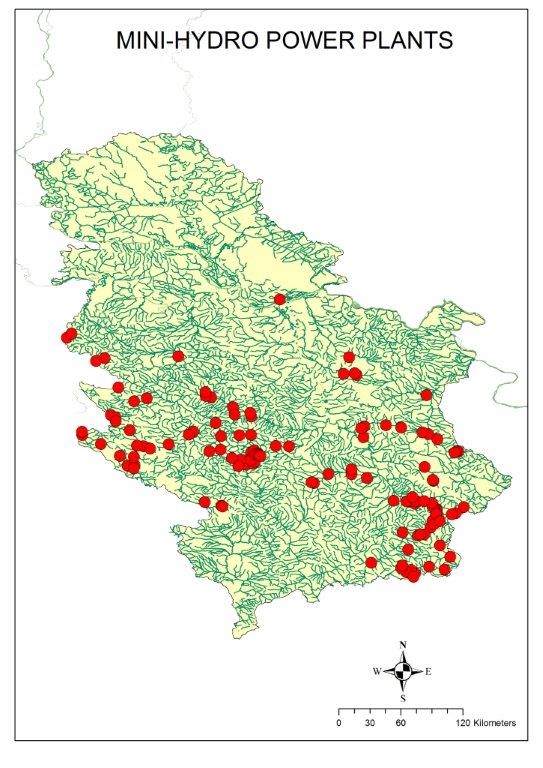
Key message: Since 2010, 126 derivative small hydro power plants have been built
Assessment: Unlike large rivers on which powerful power plants are built, where the engineering building is located in the barrier itself, small rivers and creeks do not have enough water mass for this method of electricity generation. Such river bodies are typical for the construction of small hydro power plants. In the case of derivative small hydropower plants, lacks in water mass are substituted by wide tubes buried in the trenches along the riverbed. This is done to increase velocity of water in use down to the engineering room located downstream, where the current is produced. They are built in mountainous areas because of the natural inclination of the terrain. Their construction is not expensive, and is subject to state aid which makes them harmful incentives to biodiversity. Based on data of the Register of privileged electricity producers (http://mre.gov.rs/doc/registar-020818.html), 126 derivative small hydro power plants have been built in Serbia since 2010. There is a trend of increasing the number of small hydro power plants.
However, due to the potentially harmful effect of the derivative small hydro power plants on biodiversity, numerous activities of the civil society associations, local communities and the scientific public to limit the construction of small hydro power plants have been carried out, specifically there is a demand to ban building in protected areas. Concerns about the conservation of natural resources were also expressed by experts in the form of an open public letter that was signed by deans of the Faculty of Forestry, Faculty of Biology, Faculty of Geography, Faculty of Mining and Geology as well as Director of the Institute for Biological Research “Siniša Stanković”. The letter states that an unacceptable activity is related to the use of the area in the “Stara Planina” Nature Park with unique ecosystems and the biodiversity of brown trout fish, as well as numerous other groups of plants and animals that represent a common good for the local population and all citizens of our country. The experts warned that planned construction of 58 small hydro power plants in Stara Planina region would endanger traditional way of life, livelihood of the remaining inhabitants in villages with protected cultural and historical goods. When it comes to domicile surface waters, Serbia is the poorest country in the Balkans. Water abundance of our country is under the additional negative effects of numerous polluters, bad management, and above all, the massive construction of mall hydro power plants threatening to completely destroy the remaining valuable resources, as stated in the letter. “We fully understand the obligation to partly replace energy production at the expense of fossil fuels with “green” energy derived from renewable sources. However, small hydro power plants are more than modest energy producers: if all 856 facilities were built, according to the existing Cadastre, up to 3.5% of the required amount of electricity would be provided at the annual level, but at the same time, the most valuable hill-mountain watercourses would be destroyed (an example of the Jošanička River on Kopaonik slopes), with the disturbance of the area, bio and geodiversity,” the professors warned. In the letter, they reminded that Serbia and the Balkan region are one of the most important areas of diversity of brown trout in Europe, and that mini-hydro power plants are built on these rivers. The fish passes built on these plants serve only to satisfy formal obligations, having no purpose since brown trout is not a migratory species and does not use them. In addition, the change in water regime affects the alteration and destruction of river habitats with flora and fauna, the natural hatcheries of fish, and the change in the volume and dynamics of erosion in the river bed. In addition, the regime of sprout cultivation with water from the river bed (which is introduced in the pipeline) is disturbed, so there is a decrease in the volume or drying of local wells, which also endangers the water supply of the population – the letter states with a remark: “All this is manifested in the experience of Western European countries, and in particular small hydro power plants in the Alpine regions of Germany, Austria, Italy and France, which has prompted numerous discussions in these countries, as well as at the level of the European Union on the minor energy benefits of small hydro power plants, and the large and disproportionate ecological damage that they cause. As a country with insufficient funds, we have to draw lessons from the mistakes of others, and not foolishly rush to make our own.” Four Deans of the University of Belgrade and Director of the Institute for Biological Research at the end of their address have pointed out that today there are more efficient and cost-effective, and in terms of preserving space and environment, more sustainable options for producing energy from renewable sources (wind energy, solar energy, biomass energy, geothermal, etc.). On the contrary, there is no alternative to pure water, and life without it is impossible.
Indicator Name: Small hydro power plants
Institution/Author: Environmental Protection Agency/Slaviša Popović
Use and interpretation:
Key question(s) which indicator helps to answer What is the level of impact of small hydro power plants to the environment and resources?
Use of indicator
Scale of appropriate use
Due to the potentially harmful effect of the derivative small hydro power plant on biodiversity, numerous activities of the civil society associations, local communities and the scientific public to limit the construction of small hydro power plants have been carried out, specifically there is a demand to ban building in protected areas. Concerns about the conservation of natural resources were also expressed by experts in the form of an open public letter signed by deans of the Faculty of Forestry, Faculty of Biology, Faculty of Geography, Faculty of Mining and Geology, as well as Director of the Institute for Biological Research “Siniša Stanković”.
Potential for aggregation:
Meaning of upward or downward trends (“good or bad”)
Unlike large rivers on which powerful power plants are built, where the engineering building is located in the barrier itself, small rivers and creeks do not have enough water mass for this method of electricity generation. Small hydro power plants are built on these river bodies.
Possible reasons for upward or downward trends:
In the case of derivative small hydropower plants, lacks in water mass are substituted by wide tubes, which are buried in the trenches along the riverbed. This is in order to increase velocity of water in use down to the engineering room located downstream, where the current is produced. They are built in mountainous areas because of the natural inclination of the terrain. Their construction is not expensive and is subject to state aid which makes them harmful incentives to biodiversity. Based on the data of the Register of privileged electricity producers (http://mre.gov.rs/doc/registar-020818.html), 126 derivative small hydro power plants have been built in Serbia since 2010. There is a trend of increasing the number of small hydro power plants.
Implications for biodiversity management of change in the indicator:
Possible treats and benefits on biodiversity, especially in the field of river fragmentation and migration of fishes.
Units in which it is expressed:
Number of power plants by categories (wind, hydro, biomass and biogas), by year (No)
Production capacity of electricity by categories (wind, hydro, biomass and biogas), by year (kW)
(e.g. km2, number of individuals, % change)
Description of source data:
Register of privileged electricity producers by Ministry of Energy with the data about location and capacity for production by categories
(origins, dates, units, sample size and extent, custodians)
Calculation procedure:
Number per year
kW per year
Coordinate for GIS presentations
(include appropriate methods and constraints for aggregation):
Most effective forms of presentation:
Graph, maps,
(graph types, maps, narratives, etc.-give examples where possible):
Limits to usefulness and accuracy:
(e.g. slow change in response to pressures, poor quality data, limited scope for updating)
Updating the indicator:
Yearly
(How often? What is the process?)
Closely related indicators
River fragmentation index
Energy production
Additional information and comments
Table: Trend of number of built small hydro power plants
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | total | |||
| Hydro power plants | 12 | 4 | 5 | 12 | 13 | 9 | 16 | 30 | 25 | 126 | ||
| Hydro power plants (kW) | 3327 | 2091 | 3078 | 15344 | 10836 | 4360 | 7986 | 18014 | 17246 | 82282 | ||
Serbia