Key message: The greatest damage from forest fires was in 2003, 2012 and 2016
Assessment: Forest fires are monitored every year and data are expressed in cubic meters of timber volume or hectares of land destroyed. It is evidenced that some years were specific related to damage caused by forest fires. The most remarkable damages in cubic meters of timber were in 2012, 2003 and 2011. In 2007, even the number of cubic meters of burned timber was not large, damage in hectares on forest surface caused by fires was quite expressive.
Forest fires are one of the most important forms of forest damages. Unlike controlled burning, which may lead to increased biodiversity of species, uncontrolled forest fires have highly negative effects on the ecosystem: desertification, erosion, and water loss. Climate change, i.e. alternating dry and rainy periods, is increasingly causing the problem of forest fires and incurring damage to forests in the form of natural disasters. Also, direct damage in terms of the lost timber does not have such a large importance as the loss of beneficial functions of forests after fires (hydrological, protection, climate, hygiene and health care, tourist recreational and so on).
Figure: Damage caused by forest fires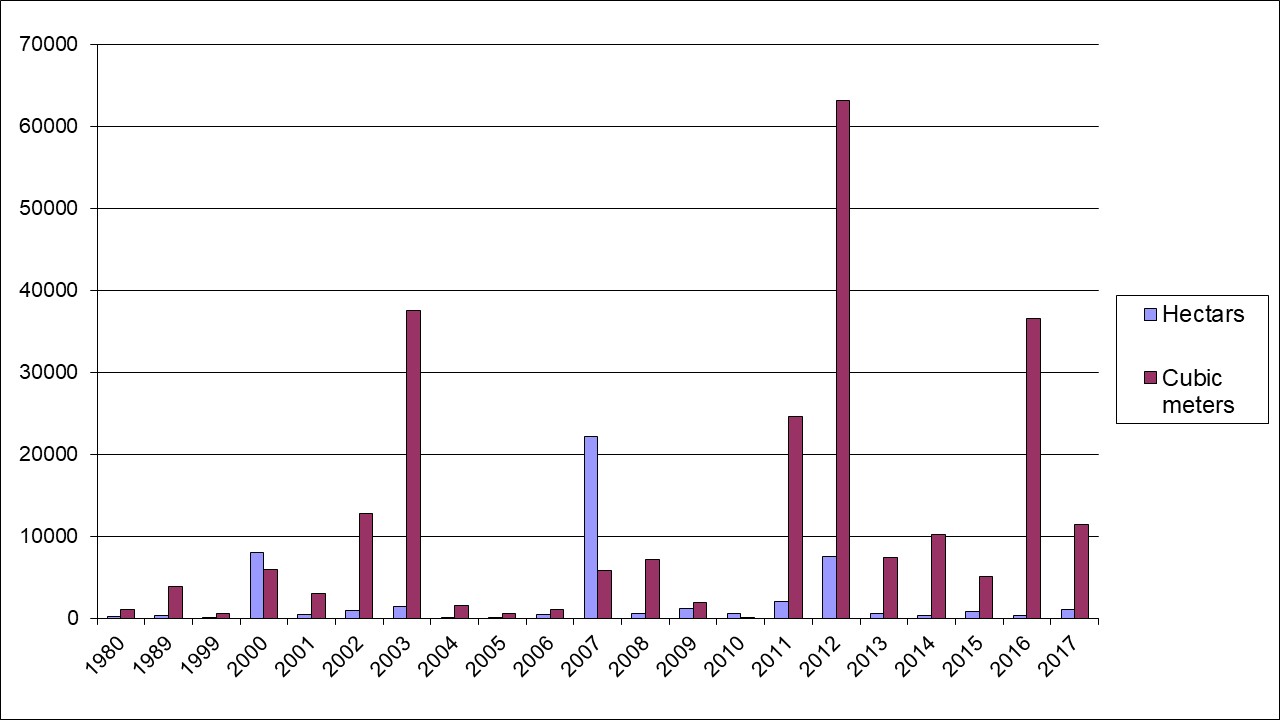
Indicator Name: Forest fires
Institution/Author: Environmental Protection Agency/Slaviša Popović
Use and interpretation:
The indicator monitors damage caused by forest fires, expressed in cubic meters and hectares.
Key question(s) which indicator helps to answer
The indicator helps to answer two questions: How many hectares of forests are damaged by fire? How many cubic meters of wood are destroyed by fire? What is the impact of forest fires on biodiversity?
Use of indicator
Forest fires are one of the most important forms of forest damages. Although controlled burning may lead to increased biodiversity of species, uncontrolled forest fires have very negative effects on the ecosystem, by intensifying desertification, erosion and water loss.
Changes in climate which are reflected in alternating dry and rain periods, increase the problem of forest fires and cause damage to forests in the form of natural disasters. Also, direct damage in terms of the lost timber does not have such a large importance as the loss of beneficial functions of forests after fires (hydrological, protection, climate, hygiene and health care, tourist recreational etc.).
Scale of appropriate use
Forest fires are monitored every year and data are expressed in cubic meters of timber volume or hectares of land destroyed.
Potential for aggregation:
Meaning of upward or downward trends (“good or bad”)
It is evidenced that some years were specific related to damage caused by forest fires. The most remarkable damages in cubic meters of timber were in 2012, 2003 and 2011. In 2007 even the amount of cubic meters of burned timber was not large, but damage in hectares on forest surface caused by fires was highly expressive.
During 2017, 11,415 cubic meters of timber volume burned, which is about 3 times less than in 2016 (37,114 cubic meters). In comparison to the previous year, when 296 ha were caught by forest fires, the surface caught by fire in 2017 amounted to 1,002 ha, which is about 3 times higher surface caught by fire.
Possible reasons for upward or downward trends:
There are two possible reasons might be crucial for trends observed related to damages caused by forest fires. One is related to climate changes and natural disasters, the second one relates to man-made damages. Compared to Forest damages indicator, man-made damage decreased by about 8% in 2015, in regards to 2014. The pressure on the forests was also maintained by intensive tourism and recreation activities which caused forest fires.
Implications for biodiversity management of change in the indicator:
The indicator is traditionally described in annual state of the environment reports in Serbia, and it is determined as biodiversity indicator, according to The Rulebook on the National list of environmental protection indicators (Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia No. 37/2011).
Units in which it is expressed:
The indicator is expressed in hectares (ha) or cubic meters (m3)
Description of source data:
Republic Statistical Office
Calculation procedure:
Methodology according to the criteria of ICP Forests, UNECE / FAO, DG Environment. Methodology defined by the Republic Statistical Office.
Most effective forms of presentation:
(graph types, maps, narratives, etc.-give examples where possible):
The best way to present this indicator is a graph.
Limits to usefulness and accuracy:
The data are obtained by the complete coverage of the reporting units of the Statistical Office. The accuracy of the data can be assessed as satisfactory. Precision depends exclusively on the delivery of data by all forest users.
Updating the indicator:
Data are updated annually.
Closely related indicators
Forest damages
Additional information and comments
Table: Damage caused by forest fires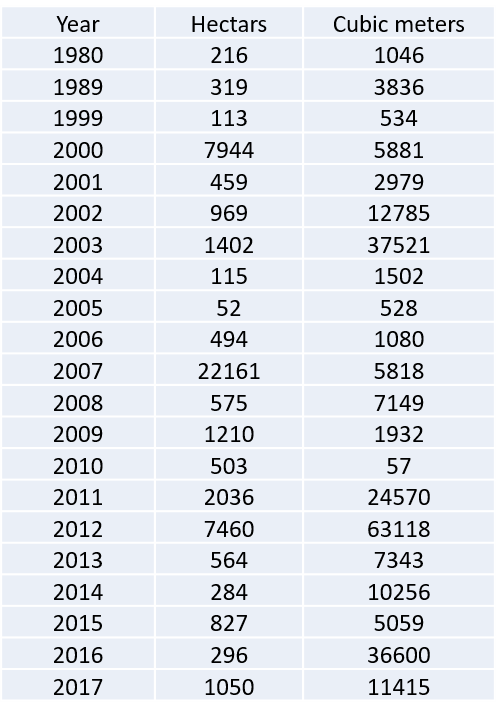
Serbia